Market Identification
In this page you will find the unit n.2, where we talk about market identification, the unit is divided in 9 module that you can find down here:
- - Marketing/Promotion & E-Commerce
- - Buisness Plan, Budgeting and Management Skills
- - Financial management in micro-enterprises
- - EU programme awareness/grants for rural micro-enterprise
- - Access to non-grant finance for micro enterprises in rural areas
- - Building Capacity in Rural Micro-Enterprises
- - Pathways2market e costumer identification
- - EU Single Market Opportunities for Rural Micro-Enterprises
- - ICT Literacy for Rural Micro-Enterprises
Now let's start with the unit 2, under here you can see al the modules which can be opened and closed all the time you want and they are ordered froom the first to the last. Now go on and learn more about marketing.
- Objective of this module:
What is promotion?
- Promotion is a mix of Actions used to increase product/service sales through leads generations
- It is one of the four elements (4 P’s) of Marketing: (Product, Price, Placement,Promotion)
- To present product/service information to consumers and others.
- To increase demand.
- Product differentation.

What is the promotional plan (mix)
- It refers to the intensity (in terms of time, effort and spending) that each promotional type is being used
Types of promotion
- Personal Selling. In-person sales, transactions made between sales representatives and clients.

- Advertising. Either audio, visual or printed. It employs an openly sponsored, nonpersonal message to promote or sell a product, service or idea.

- Sales Promotion. It includes demand raising actions such as contests, coupons, freebies, loss leaders, point of purchase displays, premium prizes, product samples, and rebates.

- Direct Marketing. Includes communication with customers through a variety of media e.g. cell phone text messagging, email, websites, online adverts, database marketing,fliers, catalogue distributio, promotional letters

- Publicity. Refers to gaining public visibility or awareness for a product, service or your company via the media.
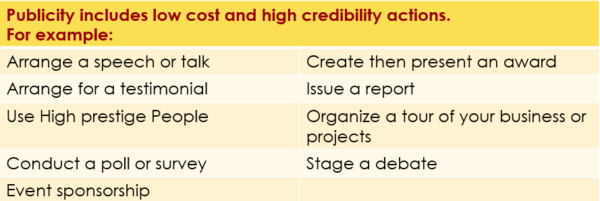
Examples of promotion tactics in the area of publicity :
Estabilishing a Promotional Mix (1 of 2)
- Target Market Determination
- Determination of objectives
- Message Design
- Selection of promotional Channels
- Budget Determination
Estabilishing a Promotional Mix (2 of 2)
Example 1 : Jeweller’s promotional mix based on a budget of 5.000 Euros
Example 2 : Candy bar that fights tooth decay with 5.000 Euros budget
Top Promotional Activities Include:
1. DOVE
Dove doubled profits from 1 to 2bn and turned the business of selling soap into a moral campaign
How
Created a mock-up advert using all of the company directors’ own daughters. With text alongside each image saying how these girls believed they weren’t beautiful, based o the existing images / models used in existing promotions, since their self-esteem was affected. Promotion strategy changd with more average girl model type.

2. NORDSTROM
A fashion retailer with $ 8,000 life-time spending per customer
How
Creating “Nordy Stories” , examples of great customer service from its employees. “Nordy Stories” give concrete examples to the employees to show them exactly how good customer service is given.
Example: A customer came into Nordstrom wishing to return a $17 tyre iron, without a receipt and in spite of the fact that the company doesn’t sell tyre irons the customer receives full refund.
(They know that the Nordstorm customer has an average lifetime spend of $8,000. What’s $17 compared to that?)

3. GE
2 million views of Videos on Company Web-site after replacing heavy mission statements
How
The human brain process visuals 50 times faster than text. Customers were attracted by the new appealing company presentation and used multichannel communication (YouTube etc.) to spread the word!

- Objective of this module:
– Financial plan as a part of Business plan
- The financial part of the business plan is one of the most important parts. Every microenterprise should have a business plan with a detailed financial plan included.
- The financial plan is constructed using: income statement, balance sheet, cash flow and budget. All these document contain essential information for the managers.
- The Balance sheet is a document that displays the financial situation of a company at a particular moment.
- The Income statement is a document which is constructed using all the income of the company and all expenses. This document is made for a defined period of operation of the company, usually a 12 month period. The Income Statement can also be called a Profit and Loss Account.
- The Budget is one of the crucial parts of a business plan. This module includes all items which are part of the business. This means that the budget sould be constructed by predicting costs of all these items.
- Tthe Budget will give the manager data for all costs of the company for the planning period.

Technique of making a budget
- Step 1 : The technique of making a budget includes as a first step predicition of all items. This means that all items from biggest to smallest should be placed on the list.

- Step 2 : After prediction of the items they should be placed in different sectors or units. Those units are separated by types of costs.

- Step 3 : After this step, the next one is to predict costs for the individual items. The technique for the prediction of the costs, include collecting data for costs for the items from different sources. Also, data from previous years can be taken for estiating costs for proposed items.

- Step 4 : After the collection of data for costs of items for the budget, costs should be allocated to the period of implementation or period of procurement of the item. This will give information to the manager in which period of operation of the company costs will arise in order that they have enough funds for implementation. This is the main purpose of budgeting; to plan to have the correct resources avaiable at the correct time. If the managers control the company according to the business plan they will be prepared for all situations and will take actions at the right time.
Cash Flow
- The Cash flow document is a table which includes all details of budget items and all details from income statement. This means that this is a summary of the flow of cash in and out the company.
- From this Cash flow document managers can get a better overview of the financial situation in the company. This document also can be prepared for the upcoming period. This will present a prediction of the financial situation in the upcoming period and will give the manager time to prepare for possible situations.
- Also, the Cash flow will give information about seasonality of the business and in which period will there be higher incomes or outlays in the company.
- The Cash flow can also include instalments from loans or other costs which are different from current daily working of the company. This can have crucial meaning for a business with higher seasonality, because they can ask the banks to vary instalments according with seasonality.
Objective of this module:
– Preparatory actions
- When planning a new venture, and before contacting a bank, there should be an understanding with the financial department.
- Ensure that the financial tool is necessary and that the risk is as low as possible.
- Conduct a business plan for the new venture
- Conduct a bank assessment survey
- A clear and detailed business plan that reflects the needs and intentions of the business will help the bank to give the right information to select the right financial tool
Bankability
- Banks have become interested in co-operating with micro-enterprises, having greater flexibility in terms of lending. This is a point that small businesses should take advantage of, by working with them to make sure they have got the right borrowing solution.

- A large part of the world economy is occupied by the agricultural sector. The high-level bank officials know that a small agri-business today could become a profitable production unit as a result of making good investments. So, what a bank is looking at is whether the business plan in bankable or not; in short, if it will create revenue for the business and therefore the bank

Building Relationships
- Building succesful banking relationships is the key to getting somethig more than easy lending. You get trusted advisios who can guide you to finding creative ways to raise finance.
- Consulting with a trustworthy financial institution, the micro-enterprises can be guided to financial solutions they may not have otherwise thought of, such as: smart use of credit cards, lease rather than buy equipment etc.
Negotiation
- Gain a clear understanding of all the terms involved so there are no surprises
- Start by looking at whether an existing product can be used, then consider modifying an existing product to meet requirments, and only consider new products or unique arrangements as a last resort
- Banks may be eager to force enterprises to use newer products, but be aware they are less likely to be familiar or cofortable with these mechanisms.
- Always begin negotiations with high-level bank officials who have real decision making ability
- Banks may want to broaden their relationships by acquiring a share of an agency’s noral banking operations, If no prior banking relationship exists, it’s important to take careful steps when discussing future partnerships.
- Clearly define the roles, responsabilities, risk mitigation and problem-solving mechanisms and counication protocols within the partnership. Set clear levels and timeframes for service delivery.
-

Types of financing
- Short-term loans: Short terms loans that most often do not require a guarantee
- Term loans: The duration of the loan is determined when the agreement is concluded. Usually repayements are made in monthly installments.
- Bank credit: The bank and the entrepreneur have agreed on a credit amout. The entrepreneur can use all or part of the amount for the needs of the business. The credit has an expiry date.
- Line of credit: The agreement is the same as the previous one but the entrepreneur may request the renewal of te credit after the expiry of the first agreement.
- Mortgages: Real estate mortgage loans are given to business that have real estate and can use it as collateral. There are two cases:
- The first case concerns the mortgaging of new property, such as the building housing the business. The property is the guarantee of the loan.
- The second case concerns property that has not yet been settled but can be used in part as a guarantee. The difference between the remaining debt and the value of the propery can be a guarantee for borrowing.
- Inventory Funding: In this case, the loan is secured by the goods in the store or in the business, provided that they have been paid for. In these cases, creditores give loans of no more than 50% of the value of the goods.

Sources of financial support
- All entrepreneurs must know the sources of financial support avaiable to them and now each of them fits with their business.
- One source of financial support is the capital of the company and the second source of financial support is the bank. It is very important to investigate the real cost of these sources at both economic and property level.
- Matching financial sources with business need is very important. The entrepreneur should remember that the best source of funding is the one that meets the needs of the business at the lowest possible cost.
What micro-enterprises should avoid
- A business plan that involves a high-level risk
- Mismanagement of the business
- An unreliable credit profile

Principles of borrowing
- Entrepreneurs should avoid borrowing more money than they need.
- Entrepreneurs should not only borrow because they are afraid of losing the opportunity to invest with third-party money.
- The loan should be neither too small to cover a large part of the needs nor too large to maximize the risk.

Objective of this module:
– EU Sources of Funds
- European Regional Development fund (ERDF) – imbalances between regions. Its key themes include innovation research, support for SMEs and digital technologies.
- European Social Fund (ESF) – Access to employment and professional skills.
- European Cohesion Fund (ECF) – Reduce economic and social disparities between EU members. Its key themes are transport infrastructure and energy.
- European Agricultural Fund for Rural Development (EAFRD) – Improve the competivitness of agriculture and forestry. Its key themes are boosting economic activity and quality of life in rural areas.
- European Maritime and Fisheries Fund (EMFF) – Supports the transition to sustainable fishing. Its key theme help coastal communities diversify their economy.
- Erasmus for Young Entrepreneurs (EYE) – An exchange programme for new and aspiring entrepreneurs.
- Creative Europe – Provides support for the cultural, creative and media sectors.
ERDF In Ireland
- Regional Assemblies ( Southern and Northern & Western) manage ERDF in Ireland
- Regional Assemblies act as the contact points.
ERDF Programmes
- Cross Border:
– Ireland/Northern Ireland/Scotland Programme
– Ireland/Wales Programme
- Transnational:
– Atlantic Area Programme
– Northern Periphery and Arctic
– North West Europe Programme
- Inter-regional:
– ESPON
– URBACT

ESF in Ireland
- Key areas – activation of the unemployed, social inclusion, education and youth employement
- Supports a range courses, schemes and projects
- Assistance channelled through Government Departments and Agencies
- Details of ESF support can be found at http://www.esf.ie/en/
ECF in Ireland
- 1.2 billion of euros of Cohesion policy funding – Ireland 2014-2020.
- 951 million of euros for ERDF and ESF co-funded programmes.
- Balance to European Territorial Cooperation (ETC) programes, e.g INTERREG and PEACE Programmes
- More information on European Cohesian Fund at http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/en/information/publications/factsheets/2014/cohesion-policy-and-ireland
EAFRD in Ireland
- More information at: https://www.agriculture.gov.ie/media/migration/ ruralenvironment/ruraldevelopment/ruraldevelopmentprogramme2014= 2020/SummaryBookletSept16290916.pdf

EMFF in Ireland
- Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine is responsible for managing this fund
- Details at http://www.agriculture.gov.ie/media/migration/seafood/ marineagenciesandprogrammes/emff/EMFFOPSummary251116.pdf

EYE in Ireland
- EYE for new entrepreneurs – less than 3 years of business experience or planning to start up a business.
- A placement, 1-3 months to another European country company supported by monthly grant.
- There are currently 5 participating partners in Ireland http://www.erasmus-entrepreneurs.eu/page.php? cid=5&pid=018&ctrIE&country=Ireland

Creative Europe Ireland
- Creative Europe Ireland provides fuding under 3 headings:
– Culture: arts, craft, design and heritage fields across Europe to reach new audiences and to develop skills needed.
– Media: supports European film and audio-visual industries in development, distribution and promotion
– Cross Sector: funding for activities common to both above.
- Information at http://www.creativeeuropeireland.eu/

Horizon 2020 in Ireland
- Horizon 2020 – EU research and innovation programme.
- 80 billion of euros 2014-2020
- Take ideas from the lab to the market
- Dedicated portal for Ireland at http://ec.europa.eu/research/horizon2020/index_en.cfm?pg=country-profiles-detail&ctry=ireland
Horizon 2020: Focus on SMEs in Ireland
- Strong participation by SMEs 20% of the budget for SMEs
- A dedicated activity for research-intensive and Innovation in SMEs
- For more information: http://ec.europa.eu/programmes/horizon2020/sites/horizon202/files/Facsheet_SME_H2020_Nov2015-pdf

Tips to identify the right funding calls
- Be clear about your field of expertise and capabilities
- Align your proposal to EU’s priorities
- Align your proposal to your organisation’s strategy
- Get in touch with your national contact point
- Attend information days for particular funding calls.
- Subscribe to the RSS feed for relevant calls and Scan for open calls
- Get assistance in the preparation of a competitive proposal
- Check if you can benefit from national subsidies to help you make your project proposal
More Information
- in Ireland more information can be found at
- Find out more about LEADER funding in other EU countries at
- The European LAG database can be found at https://enrd.ec.europa.eu/general-info/whos-who/rural-assembly-category_en#leader
Objective of this module:

– Non-grant finance and business planning (1 of 10)

– Non-grant finance and business planning (2 of 10)
For this purpose micro-enterprises must have a good financial plan and also a back up for all possible contingencies that might affect cash-flow.
– Non-grant finance and business planning (3 of 10)
– Non-grant finance and business planning (4 of 10)
– Non-grant finance and business planning (5 of 10)
– Non-grant finance and business planning (6 of 10)

– Non-grant finance and business planning (7 of 10)
– Non-grant finance and business planning (8-9 of 10)
- The Executive Sumary
- Business Overview
- Operations Plan
- Market Analysis
- Products and Services
- Sales and Marketing
- Competitive Analysis
- Management Team
- Financial plan
- Projection
– Non-grant finance and business planning (10 of 10)
Those are the parameters which will be analyzed in detail by every financial institution when looking at a loan application.

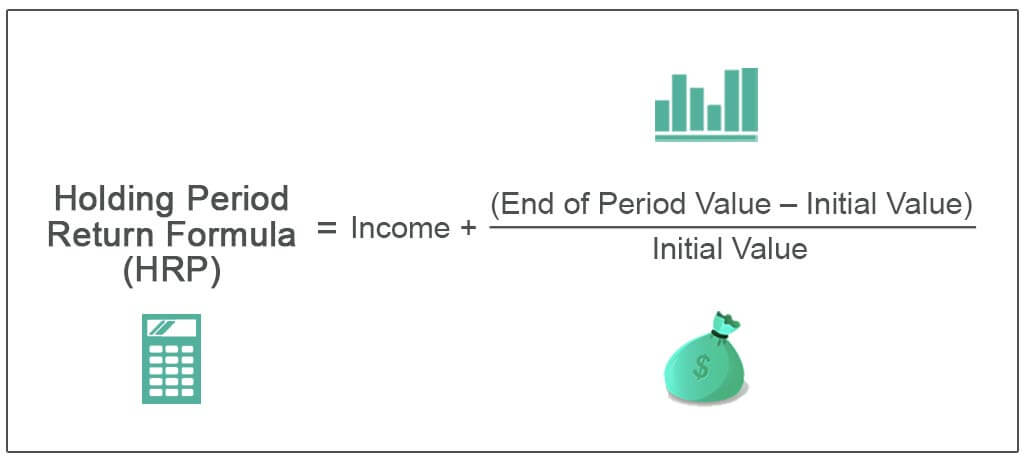
Managing the period of return of the investment
- One of the most important parameters for investors or banks is the period of return of the investments. This means that the micro-enterprises with biggest potential for growth will be a target for these financial institutions.
- What period the micro-enterprise can return the investment will determine the terms of the loan in terms of interest rate and repayement schedule (maturity). If the financial institution decides that the risk is lower, then the terms of the loan will be also more flexible and with smaller interest rate.
Objective of this module:
– What is a network
- Noun: A network is a group or system of interconnected people or things
- Verb: Networking is the skill of interacting with others to exchange information and develop professional or social contacts
- Enterpreneurs that share common goals, and intentionally exchange information and/or engage collaboratively in activities to address those goals are networks.
- May have other names: collaborative groups, social circles, mentor groups, discussion groups, learning partnerships, etc.
- You may be participating in a network without realising it – may be informal
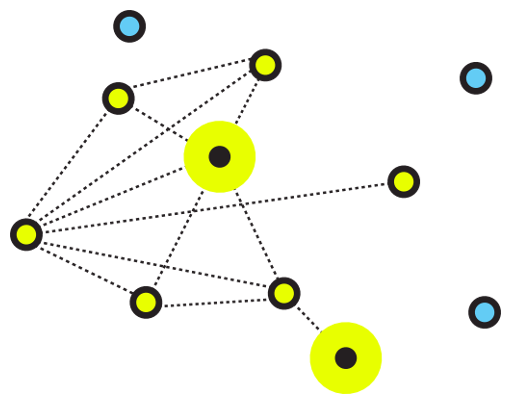
– Types of Network
Networks can range from loose informal exchanges to formal contractual or membership groups:
– Importance of networking
– Characteristics of Networks
– Type of Network to setup
- Quicker
- Ready made template avaiable
- Support of other Network members avaiable
- May not fully address your capacity requirements
- Less flexibility
- Slower
- Need to design network from scratch
- Need to seek out support from like-minded people
- Can be tailor made to your requirments
- More flexibility
– Building a small business network
– Setting up a Network
- What form will it take?
- Vision and Mission Statement for Network
- Rules of Engagement for Network:
Format of Network
- Depends on how formal the group is
- Minimum – have a chairperson and secretary for ledership and record meetings
- More formal groups need to address governance issues
- Treasurer important if fees or fundraising involved
Network Meeting Considerations
- Frequency
- Venue:
– Size required (how many members)
– Location (ease of access, distance)
– Option for virtual meetings?
- Agenda
– Consider having guest speakers
Needs Assessment for Network
- Research avaiable Networks
- Can existing network adapt/accomodate your needs?
- What type of Network is missing?
- Who in your area would be interested in joining this type of network?
Downloadable e-book

Networking events

- Costs
- Funding:
- Increased Access
- Increased Efficency
- Multiplier Effect
- Solidarity and Support
- Increased Visibility
- Reduced Isolation
- Incrased Credibility
Objective of this module:
– Introduction
– To whom do you want to sell it?
– Why should people buy the product or service from you?
When you have the answers to these questions, you should do two things:
- Focus on your primary market
- Research your market

– Focus on your primary market.
Many business owners fall into the trap of believing that their products or services are “for everyone” or they target “anyone interested in my services”. Some say they target small-business owners, homeowners, or stay-at-home moms. These targets are too general.
Targeting a specific market does not mean that you are excluding people who do not fit your criteria. And even if your business appeals to a broad market of diverse consumers, you need to identify who your ideal consumer is.
After yo have identified your primary market, your advertising should match that focus. Identifying your market allows you to focus your marketing strengths and brand message on a specific market that is more likely to buy from you than other markets. This is a much more affordabe, efficent and effective way to reach potential clients and generate business.
![]()
– Research your market

– Concepts for exploring your target market
Here are some concepts that you need to explore to define your target market.
Sector description: What is the current state of your sector in the target country and where it is headed? What is the market size? What are the current trends? In which life cycle stage the market is, and what is the projected growth?
Target market – While the scope of the previous section of your market analysis is general, the next step must be specific. You need to establish a clear idea of your target market before you decide whether to enter or not. Lots of businesses think that everyone is their potential market, but, in fact, they are definitely not.
By narrowing in on your real customers, you will be able to direct your market entry efforts and limited resources and capacity more efficiently. How many customers do you want to sell your products to within the first year on the foreign market? This is a proportion of the market you want and can reach with your products.

– Concepts for exploring your target market (contd)
Market size: Try to estimate how much is spent annually on your product category. This will tell you the size of the potential market for your products. Estimating market numbers is probably not the most enjoyable part of the market analysis. However, it truly helps you to get a basic understanding of how big the potential market is, and whether it is big enough to start a profitable business there. There are two basic rules to follow: 1) always look for numbers from reliable sources (e.g. statistics from government or private sources, objective figures from online marketplaces etc.); and 2) stay conservative.
Total market: How many customers want/need the product or product category you plan to offer? How large is the market in terms of units sold or sales?
Serviceable market: How many customers can I reach with the sales channels I am considering to use (e.g. online marketplaces, partners etc.)? Try to estimate what is the growth rate of your total and serviceable markets. Is the number of customers growing?

Competitors: Who are your competitors targeting? Who are their current customers? You may find a niche market that they are overlooking. Understanding your competitors is important for a couple of reasons: on the one hand you would like to know who are you going to compete with, but it also helps you to unveil competition’s weaknesses.
Who are your main competitors? Are there also any secondary competitors who could impact your business? What are their strengths and weaknesses? How am I different from competitors on that market? What are my advantages and disadvantages? What are my unique features? Is there anyone offering a similar product? Be careful with a statement like “there is no competition”. It is uncommon to be in a market without competitors. If you really believe there are no competitors, ask someone to search for you. If you still don’t find any competitors, there might be a logical explanation – maybe you are targeting a market that is not viable for such products. Don’t be afraid of competition. Even if there are many competitors and the market is fragmented, it can be good news for you: you are probably offering a product that is really wanted by your potential customers
![]()

Regulations: Are there any specific regulations or restrictions on your target market? If so, what are they and how you are going to comply with them? What is the cost of compliance?
![]()
Opportunities: Are there particularly favourable times in the year to enter? Is there an opportunity to get in early to take advantage of an emerging market?
– Evaluate your decision
Determining the characteristics your potential target market and analysing this information will help you make decisions whether and how to enter. Once you’ve decided on a target market, be sure to consider these questions:

Closing remark for market identification
Don’t break down your target too far! Remember, you can have more than one niche market. Consider if your marketing message should be different for each niche. If you can reach both niches effectively with the same message, then maybe you have broken down your market too far. Also, if you find there are only 50 people that fit all of your criteria, maybe you should re-evaluate your target. The trick is to find that perfect balance.
How do I find all this information? Try searching online for research others have done on your target. Search for magazine articles and blogs that talk about or to your target market. Look for survey results, or consider conducting a survey of your own. Ask your current customers for feedback.
Identifying your target market is the hard part. Once you know who you are targeting, it is much easier to figure out which media you can use to reach them and what marketing messages will resonate with them. You will save money and get a better return on investment by defining your target audience.
Basic of market analysis for business plans
By Henning Glaser
Objective of this module:
In this unit we will have a look at the various EU Single Market opportunities and how micro-enterprises can take advantage of them
Opportunities for micro enterprises in the single EU-Market
European Funding Programmes
EU policies are implemented through a wide range of thematic programmes
They provide financial support in the form of grants for specific projects and organisations
They are designed to support EU strategies and values within and outside the EU (i.e. both in EU Member States and third countries)
European Funding Programmes for SME’s (1/2)
Micro-enterprises are eligible for grant financing through EU funding programmes that cover the full range of topics and themes:
Training
Innovation
Competitiveness
Research
Social inclusion
Environment etc.
European Funding Programmes for SME’s (2/2)
The EU Commission provides grant financing to micro –enterprises through:
- Centralised programmes: to enhance SMEs’ competitiveness and innovation capacity
- Structural funds: to support growth and employment
All funding programmes are aimed at reaching Europe 2020 objectives and priorities

Centralised programmes VS Structural funds (1/2)
Centralised programmes
Centralised programmes VS Structural funds (2/2)
Structural funds
Centralised programmes (1/3)
They are the tools to implement the common policy of the European Union:
Centralised Programmes (2/3)
They are the tools to implement the common policy of the European Union:
Centralised Programmes (3/3)
They are the tools to implement the common policy of the European Union:

Structural Funds (1/3)
Structural Funds (2/3)
They are the tools to implement the regional policy of the European Union
Structural Funds (3/3)
They are the tools to implement the regional policy of the European Union

Objective of this module:
In this unit, we will look at some ICT software specific to rural business as enabling tools empowering rural development and other microenterprise interests.
Accounting Software for Rural Businesses

Accounting Software for Micro-Enterprises

Rural Businesses Management Software

Rural Business Transaction and Planning software
Small Business Software

Here is a list of small business software at https://www.inc.com/sujan-patel/the-top-small-business-software-programs-for-2015.html
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Project Management software

Travel planning software
Resource management software
– Human Resources management:
– Enterprise Resources Planning:

Document management software:

Best Free Business Software Tools

Marketing Online Software

E-Commerce Software
Free Online Store

E-mail management Software
General management Software
Cloud storage management software
This website is made for help and train all the people who want to now about marketing and that are in rural areas, all the information are given by "MICRO".

